 Speech organs
Speech organs
There are many different forms of communication, although people generally communicate with each other through the use of speech. Speech organs are body structures that work together so that people can communicate through spoken language. Also called speech articulators, these organs are necessary in the production of the voice, or the sound produced only by humans to tell each other how they think or feel. They can be classified according to whether they are active or passive.
Unlike most animals that have the ability to communicate non-verbally, most humans produce different words to communicate with each other. The speech is delivered with great speed; Usually, a person who wants to talk doesn’t need to think too hard about what to say. When a person speaks, his thoughts are immediately converted into a spoken form as soon as the speech organs receive a signal or instruction from the brain. Thus, speech occurs when a person’s brain and speech organs work together, although the organs of the respiratory system also play an important role in this process, since the vocal cords need air to vibrate and produce sound.
A speech organ is active if it moves as sound is produced, while it is passive if there is no movement. Along with the lips, tongue, and teeth, these organs also include the alveolar crest, uvula, palate, and glottis. Of these speech articulators, only the lower lip, tongue, and glottis are active. The mechanism of sound or voice production begins when incoming air flows through the glottis, resulting in vibration of the vocal cords. This vibration pushes air to flow through the glottis to vibrate the vocal tract, producing sound.
Articulatory phonetics deals with how the organs of speech work together. For example, the interaction between the lips and the teeth can produce different sounds. Vowels are produced when the shape of the mouth changes through coordination between the upper and lower lips, although the position of the tongue is also important. Consonants are produced by coordination between the tongue, teeth, and palate.
The speech organs are also prone to stress, called vocal load, due to various factors. Continuous use of the voice, speaking loudly for a long time, and speaking with an unusual tone of voice can cause stress on the speech organs. Smoking and dehydration can cause dryness in the throat area, affecting voice quality. Vocal load can be avoided by minimizing the use of the voice, speaking at a normal volume and tone of voice, avoiding smoking, and drinking plenty of fluids.
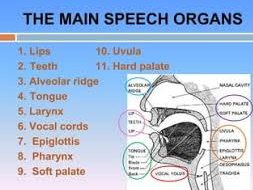
Parts of the speech apparatus
The phonetic apparatus consists of three groups of organs.
Breathing organs The Importance Of Speech Organs
Lungs
The lungs are the largest organs of the human body and their main function is to allow inspiration and expiration of air . They are formed by connective tissue inside which are the bronchial tubes, which progressively branch off from the trachea. The Importance Of Speech Organs
Bronchi
The bronchi are the ducts that arise from the bifurcation of the trachea . Each of the bronchi is connected to one of the lungs. The air enters through the trachea and reaches the lungs through the bronchi, so that its role is very important.
Windpipe
The trachea is one of the most important elements of the respiratory system. It is the tube that connects the nose and mouth with the lungs and bronchi . It is shaped like a tube and consists of a set of cartilaginous rings. It begins in the larynx and runs to the chest.
Phonation organs The Importance Of Speech Organs
Larynx
The larynx is a tubular organ formed by a total of six cartilage . Connect the pharynx with the trachea. This is the organ of phonation because the vocal cords are located in the larynx.
Vocal chords
The vocal cords are the element of the phonological apparatus responsible for the production of the voice . Despite their name, the truth is that they have no rope shape, but are a set of folds. They are a total of four, divided into two large groups: true and false . The false ones do not participate in the production of sounds, while the true ones do. The Importance Of Speech Organs
Resonators
The resonators are responsible for the vibrations that come from the vocal cords become sound.
Articulation organs
Palate The Importance Of Speech Organs
The palate is the upper wall of the oral cavity . It is divided into two parts: the bone palate and the veil of the palate. Its main function is to separate the oral cavity from the nostrils and its interaction with the tongue allows the articulation of sounds.
Language
The tongue is a mobile organ that is inside the mouth. It has a key role in numerous functions, such as mouth hydration , swallowing or language, among others. It is characterized by its cone shape.
Teeth
In the case of adults, they have a total of 32 teeth : 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 12 molars. It is interesting to know that not all adults have wisdom teeth since there is not always enough room for growth. The Importance Of Speech Organs
Lips The Importance Of Speech Organs
The lips are essential to carry out a large selection of functions, such as sucking or kissing, among others.
Glottis
The glottis is the narrowest part of what is called laryngeal light , a space limited by the vocal cords. Before the vibration of the vocal cords, the sound is transformed into voice or loudness. Thus, when they do not vibrate what is called dull sound is produced. The Importance Of Speech Organs


