What is Explanatory Research concepts objectives, examples and comparatives
Concepts and definitions of explanatory research
Explanatory research seeks to identify the causes of the phenomena studied, in addition to recording and analyzing them. This happens both through the application of experimental/mathematical methods and through the interpretation of qualitative methods.
In this way, explanatory research aims to explore something new and can be used both in scientific initiation.
Therefore, it is performed as an attempt to connect ideas, to understand the causes and effects of a given phenomenon.
Explanatory research seeks, as the name suggests, to explain what is happening .
According to Gil (2007) this type of research is concerned with identifying the factors that determine or contribute to the occurrence of phenomena.
Also, the explanatory research according to Gil (2007, p. 43), can be the continuation of another descriptive one, since the identification of factors that determine a phenomenon requires that it is sufficiently described and detailed.
The complexity of this type of research comes exactly from the fact that its objective is not only to record, analyze and interpret the phenomena studied, but also to identify their causes.
Objectives of Explanatory Research
In view of the concepts presented, the main objective of explanatory research is the need to deepen reality, through the manipulation and control of variables. That is, looking for the “why” of things.
In this sense, the scope is to identify which independent variable or the one that determines the cause of the dependent variable of the phenomenon under study and then study it in depth.
Although the results of explanatory research support scientific knowledge, due to its broad objective, it is more subject to the risk of making mistakes.
Still, we follow Gil (2019) who states that explanatory research aims to identify factors that determine or contribute to the occurrence of phenomena.
Explanatory research is more structured than other research with other scopes and, in fact, involves their purposes (exploration, description and correlation or association), in addition to providing a sense of understanding of the phenomenon to which they refer.
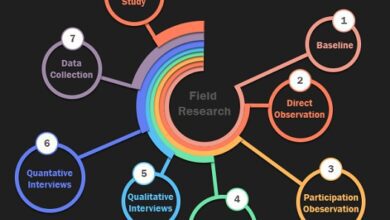
Explanatory Research Methodology
To record, analyze and interpret the phenomena studied, seeking to identify their reasons, their determining factors, their causes, most explanatory research uses the experimental method.
When performed in the natural sciences, it requires the use of the experimental method and, in the social sciences, it requires the use of the observational method.
It is not always possible to carry out rigorously explanatory research in the social sciences, but in some areas, especially in psychology, research has a high degree of control, being called “quasi-experimental” research.
This method is characterized by the manipulation and control of variables, with the objective of identifying which independent variable determines the cause of the dependent variable or the phenomenon under study.
According to Gil (2019), it can be said that scientific knowledge is based on the results offered by explanatory studies. This does not mean, however, that exploratory and descriptive research has less value, because they almost always constitute an indispensable previous step in order to obtain scientific explanations.
Sometimes research can be characterized as primarily exploratory, descriptive, correlational or explanatory, but not uniquely positioned as such.
That is, even if a research is essentially exploratory, it will contain descriptive elements; or even, a correlational study may include descriptive components, and the same happens with the other scopes.
We must also remember that research can start out being exploratory or descriptive and then be correlational or even explanatory. It all depends on the goals of the person doing the research.
Differences between documentary, experimental, exploratory, descriptive and explanatory research
Understanding the differences between the three main types of research can clarify any doubts that may hinder the development of a work.
First, note that the first two, the documentary and the experimental, are classifications in terms of procedures.
The last ones, exploratory, descriptive and explanatory, are classifications regarding objectives.
Documentary research
Documentary research is a classification regarding the Procedure.
Documentary research is based on material that has not received analytical treatment.
For example, a journalistic text can be elaborated from a material without analytical treatment, then documentary.
experimental research
First, in experimental research, an object of study is determined, and it is a classification in terms of the procedure.
According to Gil (2007), the experimental research aims to select the variables that would be able to influence the object.
In addition, ways of controlling and observing the effects that the variable produces on the object must be defined.
Exploratory research
On the other hand, exploratory research aims to provide greater familiarity with a problem and is a classification in terms of objectives .
To do so, it involves a bibliographic survey, interviews with people who have had practical experiences with the problem, in addition to the analysis of examples.
It generally takes the form of bibliographic research and case studies .
descriptive search
In turn, descriptive research aims to characterize a certain phenomenon, such as describing the characteristics of a certain population and is also a classification in terms of objectives .
Thus, establishing relationships between variables, which involves standardized data collection techniques, such as questionnaires and observation techniques.
Generally, it takes the form of a survey.
Explanatory research
The last category by objectives , explanatory research, aims to identify the factors that determine phenomena and explain why things happen.
According to Gil (2007, p. 43), an explanatory research can be the continuation of another descriptive one, since the identification of factors that determine a phenomenon requires that it is sufficiently described and detailed.
In this way, it generally assumes the forms of experimental
research and ex-post-facto research.
Examples of Explanatory Research
Below we separate three very interesting examples for you to be able to identify what explanatory research is:
- Showing constituency intentions is a descriptive activity .
Since indicating, according to an opinion poll conducted before the election, how many people “will” vote for the candidates is a descriptive research.
- Relating these intentions to concepts such as age and gender of voters or the extent of propaganda effort undertaken by candidate parties is a correlational study .
- On the other hand, in case the objective is to show why someone could vote for certain candidates and other people for the other candidates, it will be an explanatory research .
Tools for the application of explanatory research
Working with different techniques and tools for problem solving is a practical way to achieve satisfactory results within projects in academic and scientific circles.
When it comes to explanatory research, the different tools that constitute it help researchers during investigative processes, where they seek to find the factors that generate a particular problem scenario.
When these tools are used correctly, answering the whys initially raised becomes a less complex task. Because the entire analytical structure involved in solving the problem is available to those who are researching.
Among the tools available to reach a conclusive answer about the whys of a situation are:
Comparison of previously collected data
Through Documentary Research, the comparison between different data samples can clarify some issues in the analysis scenario.
Both quantitative and qualitative data can be useful to researchers.
Bibliographic research
Researching reliable sources of information can be extremely useful during the phases of an Explanatory Research.
It is interesting to question whether events similar to the one that is the subject of an investigation have already been recorded previously by other researchers ;
Use of deductive logic
deductive logic is based on the concept of looking for logical and causal motivations that result in a certain event or phenomenon. That is, which sequence of events is most likely to have provoked it.