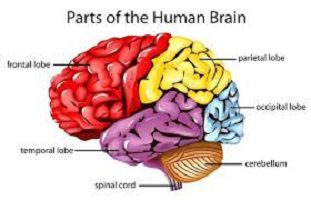
Educational psychology concept and theories with explanation
Educational psychology
Educational psychology is a subdiscipline of psychology that is responsible for studying the ways in which human learning takes place, especially in the context of educational centers. Educational psychology analyzes the ways in which we learn and teach and tries to increase the effectiveness of different educational interventions in order to optimize the process. It also tries to apply the principles and laws of social psychology to educational institutions and organizations. Educational psychology concept and theories
In other words, the object of the study of educational psychology is student learning and the different aspects that modulate their cognitive development.
Psychology is responsible for the scientific study of human behavior and mental processes. There are several different sub-disciplines of psychology that focus their focus on a particular aspect of the human psyche, in order to better understand our behavior and provide tools to improve the well-being of each individual. Educational psychology concept and theories
One of these sub-disciplines is educational psychology (also called educational psychology ), which is responsible for deepening learning and the most suitable educational methods so that students can develop their cognitive skills.
Educational psychology to improve learning
In the school context, educational psychology investigates the best methods and study plans that allow improving the educational model and the management of the centers.
Since their objective is to better understand the elements and characteristics that influence learning during childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and old age, educational psychologists are in charge of elaborating and implementing different theories about human development that help to understand the different processes and contexts in which learning occurs.
Theories about learning
Throughout the past century, several authors have proposed models and theories to explain the way in which humans relate to knowledge. These theories have served to influence the approaches and methods used by educational psychology.
1. Jean Piaget’s Theory of Learning
The Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget (1896 – 1980) has had a decisive influence on educational psychology. His theory delved into the stages that children go through in relation to their cognitive ability until they manage to develop abstract logical thinking around eleven years of age. It is one of the leading references in the field of developmental psychology.
2. The Sociocultural Theory of Lev Vygotsky
To what extent do culture and society influence children’s cognitive development? This is the question posed by the Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896 – 1934). Vygotsky investigated the influence of the different social environments in which interactions take place that lead the child to assimilate and internalize some behavior patterns.
His concepts, such as the ” proximal development zone ” and ” scaffolding learning ” are still valid today. Educational psychology concept and theories
3. Albert Bandura’s Theory of Social Learning
Albert Bandura (born 1925) also developed key concepts for sociocognitivism and for educational psychology. Bandura analyzed the intimate relationship between contextual and social variables with learning processes. In addition, he was the author of concepts of great interest such as self-concept.
Other theories and contributions
There are other theoretical constructs that have also contributed great knowledge to the field of educational psychology. For example, the theory of moral development by Lawrence Kohlberg and model child development proposed by Rudolf Steiner.
In addition to psychologists who contributed their grain of sand to educational psychology, it is also necessary to cite other authors and figures with a decisive weight and who sowed this subdiscipline with knowledge and reflections.
The role of educational psychologists
Educational (or educational) psychologists are in charge of analyzing the various characteristics of each student. This awareness of the individual differences of the students serves to try to enhance the development and learning of each of them, reflecting on intelligence, motivation, creativity, and communication skills, among other aspects.
One of the keys: motivation
A motivated student is a much more receptive student to acquire new knowledge and skills. It is for this reason that motivation is one of the favorite fields of study of educational psychology. The motivation depends on the degree of interest that the teachings in the classroom arouse, the level of involvement of the student with the tasks to be done. In addition, thanks to motivation, the student begins to acquire knowledge through meaningful learning.
Motivation does not refer only to the predisposition to learn in class, but it has a crucial influence on the aspirations and objectives of the people in their lives.
Disorders and difficulties associated with learning
Educational psychologists also have to deal with the problems some students have in learning at the same rate as their peers. School-age children can present specific difficulties such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or Dyslexia, which negatively affect the cognitive aspects related to the learning process. It will be necessary for the educational psychologist, in agreement with the teachers, to plan a study plan adapted to these cases, trying to minimize the academic impact of these disorders or delays.
However, educational psychologists also have a fundamental role in detecting and treating other problems of a non-specific nature. For example, clinical cases such as students with depression, anxiety, or any other type of affectation that requires individualized treatment and, in some cases, a curricular adaptation. Other psychosocial problems such as students affected by bullying may also require the intervention of the educational psychologist. Educational psychology concept and theories