Syntax
Syntax
Syntax is a subfield of linguistics that focuses on the study of sentence structure, word order, and the relationships between words and phrases in language. Syntax is concerned with how speakers of a language combine words to form meaningful and grammatical sentences. It is one of the central components of language and plays a crucial role in the communication of meaning.
Syntax involves the study of both the form and the function of sentences. The form of a sentence refers to its grammatical structure, including the arrangement of words and the patterns of inflection and agreement. The function of a sentence refers to its communicative purpose, such as making a statement, asking a question, or expressing an emotion.
One of the key concepts in syntax is the notion of a constituent. A constituent is a group of words that functions as a single unit within a sentence. For example, in the sentence “The cat sat on the mat,” the noun phrase “the cat” is a constituent, as is the prepositional phrase “on the mat.” Constituents are important in syntax because they can be moved around in a sentence or replaced with a pronoun without changing the overall meaning of the sentence.
Another important concept in syntax is word order. Word order refers to the arrangement of words in a sentence. Different languages have different rules for word order, and these rules can affect the meaning of a sentence. For example, in English, the basic word order is subject-verb-object, as in “The cat chased the mouse.” In Japanese, however, the basic word order is subject-object-verb, as in “The cat the mouse chased.” Changes in word order can affect the emphasis placed on different parts of a sentence and can also affect the overall meaning of the sentence.
Syntax also involves the study of grammatical categories and their relationships to one another. Grammatical categories include parts of speech such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, as well as grammatical features such as tense, aspect, and agreement. The relationships between these categories are governed by rules of syntax, which specify how they can be combined to form grammatical sentences.
Syntax also involves the study of language universals and language variation. Language universals are patterns or features that are found in all human languages, such as the existence of nouns and verbs or the use of tense and aspect. Language variation, on the other hand, refers to the ways in which different languages can vary in their syntax. For example, some languages have more complex inflectional systems than others, while others may rely more on word order to convey meaning.
Syntax is an important area of linguistics that helps us to understand how language is structured and how it is used to convey meaning. By studying the rules and patterns of sentence structure, linguists can gain insights into the nature of human language and the ways in which it is used in communication.
-

Syntax figures Pleonasm anaphora Anacoluto Ellipse and Zeugma
Syntax figures Also called construction figures , syntax figures are: Pleonasm; Anaphora; Anacoluto; Ellipse; Zeugma; Asyndeton; Polysyndeton; Anastrophe; Hyperbate; Synchisis; Hipalage; Silepsis. Syntax…
Read More » -

Deductive syntax semantic layer and Scope of rules
Deductive syntax Traditional Grammar developed a syntax based on the analysis of well-formed sentences given a priori. That is, it starts…
Read More » -
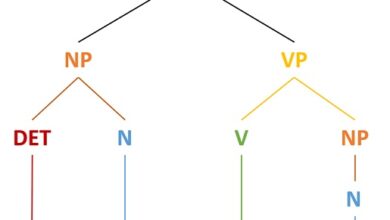
Syntactic structures Formal units Unit Fittings and Delimitation
Syntactic structures When studying language, we only have discourses as a starting point. The grammar of the language is not visible…
Read More » -
Morphosyntactic analysis of a sentence
The morphosyntax comprises an analysis made to clauses from syntactic and morphological terms. Therefore, morphosyntax will comprise a complete analysis, covering…
Read More » -
Syntactic Analysis Simple Sentences with Examples
Syntactic analysis Syntactic analysis is the study of the function of each term in a sentence. A term, or word,…
Read More » -
Apposition in grammar with types and 50 examples
Apposition An apposition is a clarification that modifies the head of a noun phrase and provides information to specify it. For example: Mario, my husband, got…
Read More » -
Verb phrases in English with examples and structures
Verb Phrase A verb phrase is the combination of the main verb and one or more auxiliary verbs. In this article we…
Read More » -
Prepositional Phrases with formation and Illustration
Prepositional Phrases The prepositional phrases [prepositional phrases] are the combination of prepositions and other sentence elements. We use them as adjectives,…
Read More » -
Adjective phrase examples and formation of adjective phrase
Adjective Phrases The adjective phrases are sets of words used to describe or qualify something. The core of this set of words is…
Read More » -
Noun phrases examples with Modifiers and functions
Noun phrase A noun phrase is a structure that has a noun , a pronoun , or a noun word as its head or higher-ranking element. For…
Read More »